"We've discovered the secret of life!" - Francis Crick
"We've discovered the secret of life!"
- Francis Crick
In 1953, Francis Crick and James Watson first discovered the structure of DNA: a double helix! Their breakthrough came over lunch at The Eagle pub in Cambridge after they finished assembling their cardboard-and-metal model at the Cavendish Laboratory. Using Rosalind Franklin’s crucial Photograph 51—shown to Watson by Maurice Wilkins without her knowledge—they recognized that DNA formed two complementary strands twisted into a helix. Their 1953 Nature paper ended with the understated observation that base-pairing suggested a copying mechanism for genetic material, quietly ushering in modern molecular biology. Crick, Watson, and Wilkins later won the 1962 Nobel Prize, while Franklin’s untimely death prevented her from sharing the honor.
What is DNA?
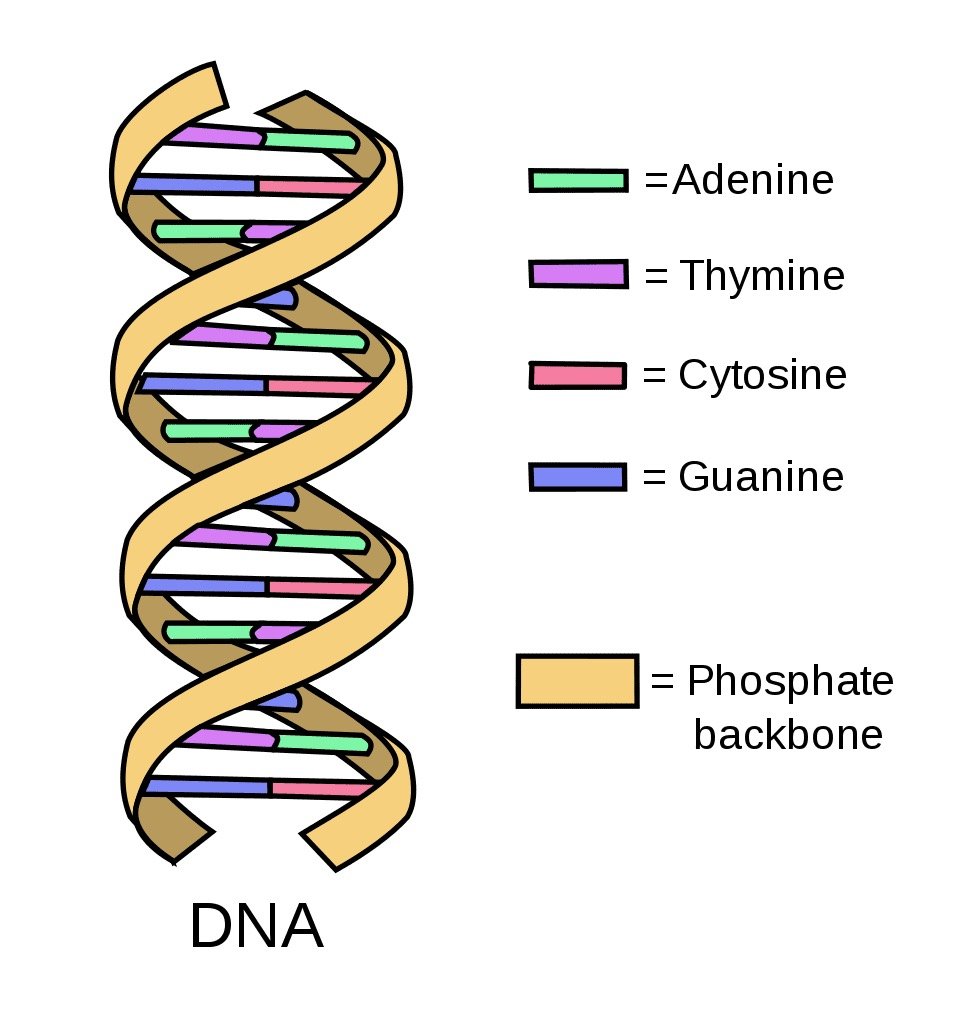
DNA, also known as deoxyribonucleic acid, is made of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder. This shape is known as a double helix. Just like a computer uses 1s and 0s to store information, biological systems use A, T, C, and G. The majority of these letters are identical in each of us.
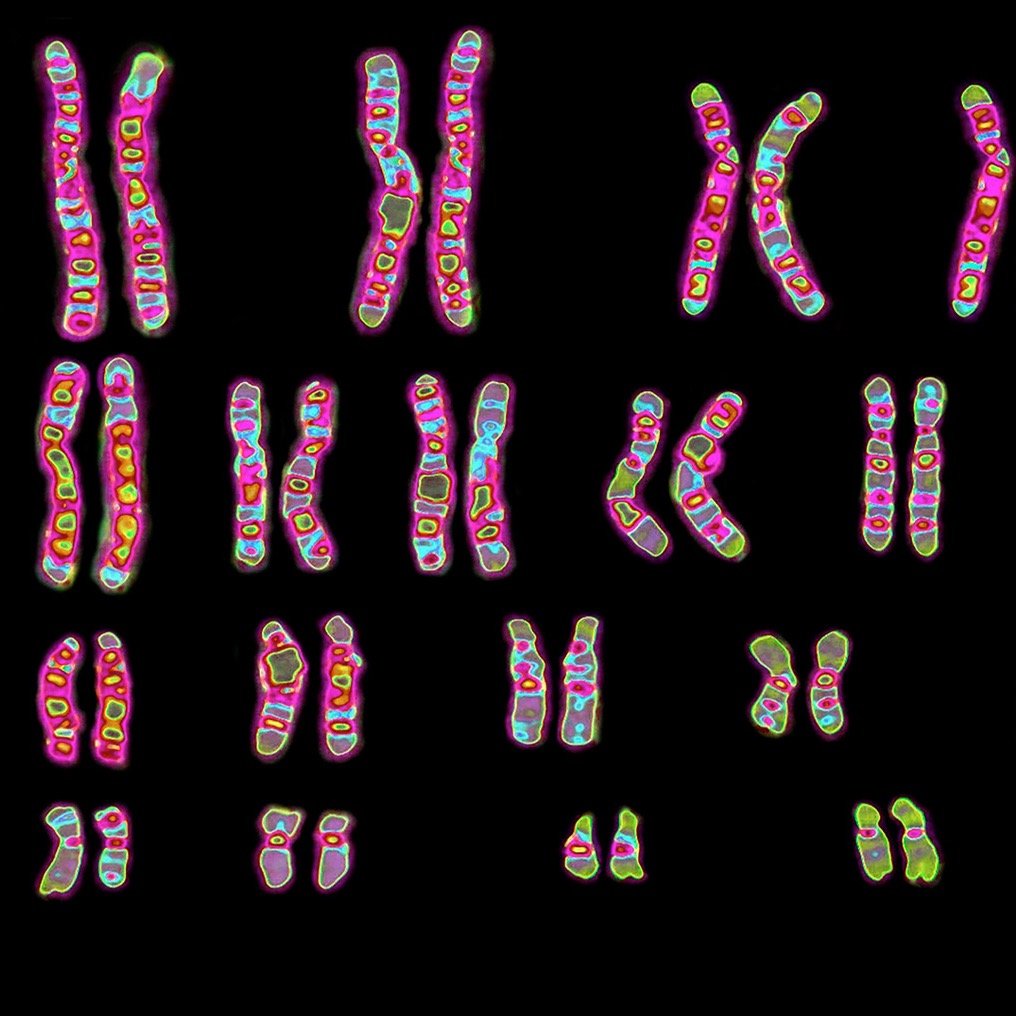
DNA is stored in a very unique way. It is coiled tightly into structures known as chromosomes. Condensing DNA in this manner is an efficient way to store biological information. On average, humans have 46 of these structures in each and every cell. Your genome, also known as your entire genetic code, can be found in just one cell!

What is a genetic mutation?
A mutation is a permanent change in the DNA sequence of a cell or organism. At these locations, you can expect to find different base pairs (A, C, G, and T are bases), extra base pairs, or even missing base pairs. Mutations can be harmful, beneficial, or have no effect, and they can occur in body cells or in reproductive cells. At MyGenetics, we test the DNA of cheek cells.
What can a mutation do?
When someone has a mutation, this can lead to changes in how their body works. For example, let’s say a certain region in their genome codes (helps make) for a protein. Altering the genetic code here can change the structure of the protein getting fabricated. Since function depends on structure, this will lead to a different type of protein capable of behaving differently.
